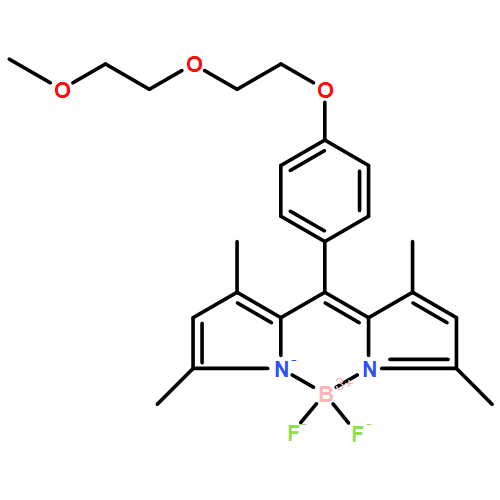
Co-reporter: Xiuyu Yi, Jianzhang Zhao, Jifu Sun, Song Guo and Hongli Zhang
pp: 2062-2074
Publication Date(Web):06 Nov 2012
DOI: 10.1039/C2DT32420B
We prepared N^N Re(I) tricarbonyl chloride complexes (Re-1 and Re-2) that give very strong absorption of visible light. To this end, it is for the first time that boron dipyrimethane (Bodipy) was used to prepare Re(I) tricarbonyl chloride complexes. The π-conjugation linker between the π-conjugation framework of the antenna Bodipy and the Re(I) coordination centre ensures efficient intersystem crossing (ISC). Re-0 without visible light-harvesting ligand was prepared as a model complex in the photophysical studies. Re-1 (with Bodipy) and Re-2 (with carbazole-ethynyl Bodipy) show unprecedented strong absorption of visible light at 536 nm (ε = 91700 M−1 cm−1) and 574 nm (ε = 64600 M−1 cm−1), respectively. Interestingly, different from Re-0, Re-1 and Re-2 show fluorescence of the ligand, not the phosphorescence of the Re(I) coordination centre. However, long-lived triplet excited states were observed upon visible light excitation (τT = 104.0 μs for Re-1; τT = 127.2 μs for Re-2) vs. the short lifetime of Re-0 (τT = 26 ns). With nanosecond time-resolved transient absorption spectroscopy and DFT calculations, we proved that the triplet excited states of Re-1 and Re-2 are localized on the Bodipy ligands. The complexes were used as triplet photosensitizers for two triplet–triplet-energy-transfer (TTET) processes, i.e.1O2 mediated photooxidation and triplet–triplet annihilation (TTA) upconversion. With the strong visible light-harvesting ability, Re-1 proved to be a better 1O2 photosensitizer than the conventional triplet photosensitizer tetraphenylporphyrin (TPP). Significant upconversion was observed with Re-1 as the triplet photosensitizer. Our result is useful for preparation of Re(I) tricarbonyl chloride complexes that show strong absorption of visible light and long-lived triplet excited states and for the application of these complexes as triplet photosensitizers in photocatalysis, photodynamic therapy and TTA upconversion.
Co-reporter: Xiuyu Yi, Jianzhang Zhao, Jifu Sun, Song Guo and Hongli Zhang
pp: NaN2074-2074
Publication Date(Web):2012/11/06
DOI: 10.1039/C2DT32420B
We prepared N^N Re(I) tricarbonyl chloride complexes (Re-1 and Re-2) that give very strong absorption of visible light. To this end, it is for the first time that boron dipyrimethane (Bodipy) was used to prepare Re(I) tricarbonyl chloride complexes. The π-conjugation linker between the π-conjugation framework of the antenna Bodipy and the Re(I) coordination centre ensures efficient intersystem crossing (ISC). Re-0 without visible light-harvesting ligand was prepared as a model complex in the photophysical studies. Re-1 (with Bodipy) and Re-2 (with carbazole-ethynyl Bodipy) show unprecedented strong absorption of visible light at 536 nm (ε = 91700 M−1 cm−1) and 574 nm (ε = 64600 M−1 cm−1), respectively. Interestingly, different from Re-0, Re-1 and Re-2 show fluorescence of the ligand, not the phosphorescence of the Re(I) coordination centre. However, long-lived triplet excited states were observed upon visible light excitation (τT = 104.0 μs for Re-1; τT = 127.2 μs for Re-2) vs. the short lifetime of Re-0 (τT = 26 ns). With nanosecond time-resolved transient absorption spectroscopy and DFT calculations, we proved that the triplet excited states of Re-1 and Re-2 are localized on the Bodipy ligands. The complexes were used as triplet photosensitizers for two triplet–triplet-energy-transfer (TTET) processes, i.e.1O2 mediated photooxidation and triplet–triplet annihilation (TTA) upconversion. With the strong visible light-harvesting ability, Re-1 proved to be a better 1O2 photosensitizer than the conventional triplet photosensitizer tetraphenylporphyrin (TPP). Significant upconversion was observed with Re-1 as the triplet photosensitizer. Our result is useful for preparation of Re(I) tricarbonyl chloride complexes that show strong absorption of visible light and long-lived triplet excited states and for the application of these complexes as triplet photosensitizers in photocatalysis, photodynamic therapy and TTA upconversion.